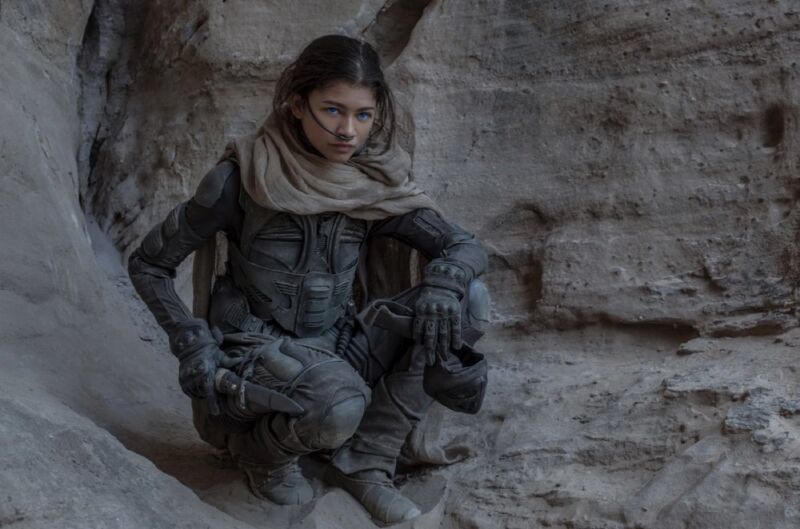

If you have watched the Dune movies, you must have noticed the ‘stillsuits ‘worn by some characters as depicted in figure 1. These suits recycle the water lost through sweat or urine by purifying it and making it potable. This is instrumental for survival as the movie franchise takes place on the desert planet of Arrakis which is almost completely void of fresh water.
Astronauts aboard the International Space Station (ISS) face similar perils as essential resources like fresh drinking water are limited. Moreover, these astronauts spend multiple hours doing spacewalks for maintenance purposes. During these long hours outside the confines of the ISS, answering nature’s call is also a complicated affair. However, researchers at Cornell University have come up with an ingenious solution to these problems and the stillsuits from the Dune movies seem to be their inspiration.
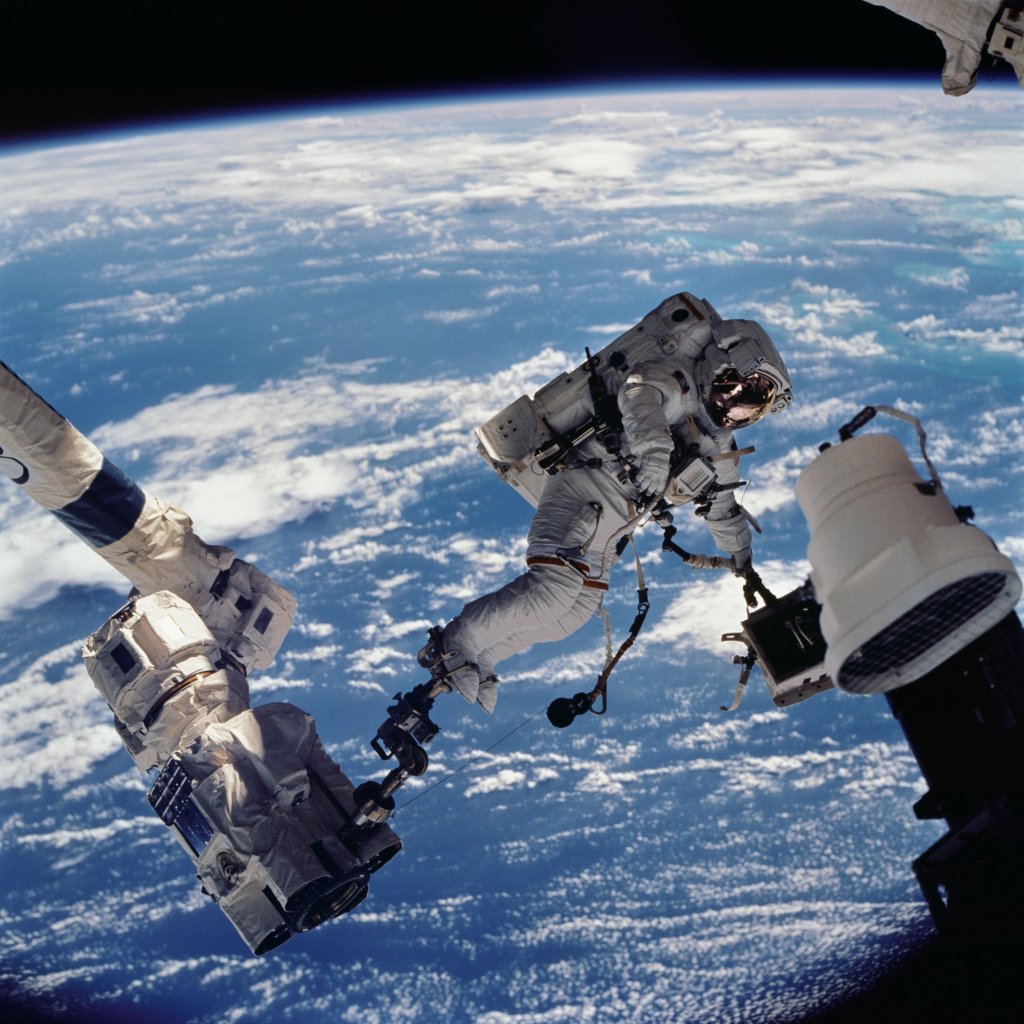

The ‘Astronaut diaper ‘ Problem
Astronauts make multiple spacewalks during their time aboard the ISS. During these spacewalks, they are required to wear a maximum absorbency garment (MAG), which in simple words is an adult diaper. According to Sofia Etlin, the co-author of this new research paper; these MAGs are known to leak leading to infections among the astronauts. Furthermore, due to the discomfort of wearing MAGs astronauts often eat less, which could ill affect their health. Additionally, astronauts carry only 1 litre of drinking water in their In-suit drink bag (IDB) attached to their space suit. This quantity may not be enough as spacewalks could last as long as 24 hours.

So what is the solution?
A proposed solution involves certain modifications to the spacesuit itself. Firstly, the MAGs will be replaced by a urine collection device (UCD). UCD consists of a urine collection cup made of silicon with a microfibre polyester lining on the inner side. This lining will draw the collected urine away from the body and provide more comfort than wearing a MAG. A vacuum pump connected to this cup sucks the urine and transfers it to the Urine filtration system (UFS). The UFS consists of a combination of forward and reverse osmosis to purify the urine water.
But what is osmosis?
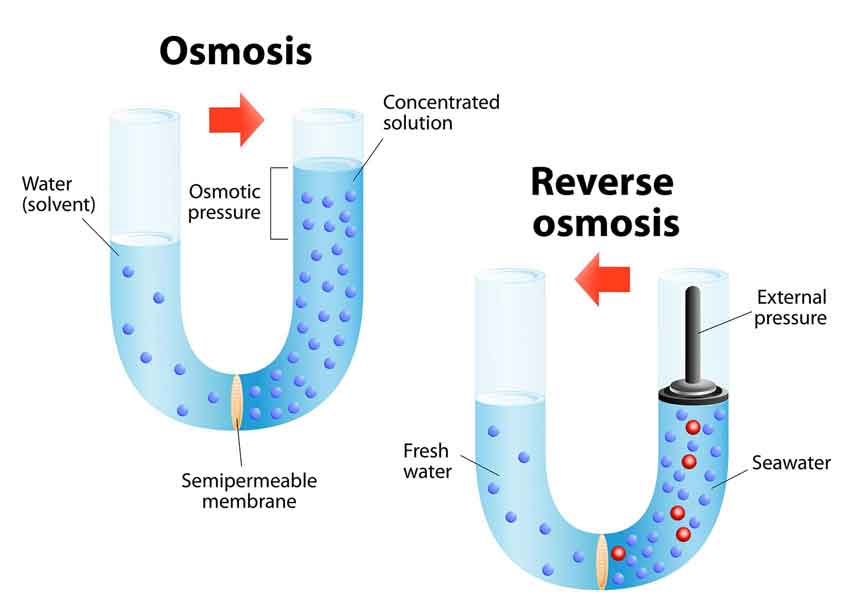
Assume two solutions are present in U – shaped tube divided by a semipermeable membrane that does not allow heavy compounds like dissolved salts to pass through. The solution on the left side of the tube is dilute or has high water potential (Water potential is the tendency of water to move from one region to another). At the same time, the one on the right is highly concentrated with dissolved salts or has lower water potential. If left undisturbed, water will start moving spontaneously from the left side of the tube to the right side through the membrane until both sides have almost equal concentrations of salts. This is called osmosis or forward osmosis (FO). Conversely, the process is called reverse osmosis (RO) when water flows from an area of low water potential to a higher water potential. Unlike FO, energy needs to be spent to carry out this process via external pressurization as it does take place spontaneously due to the resulting imbalance in salt concentration on both sides.
Working of the UFS
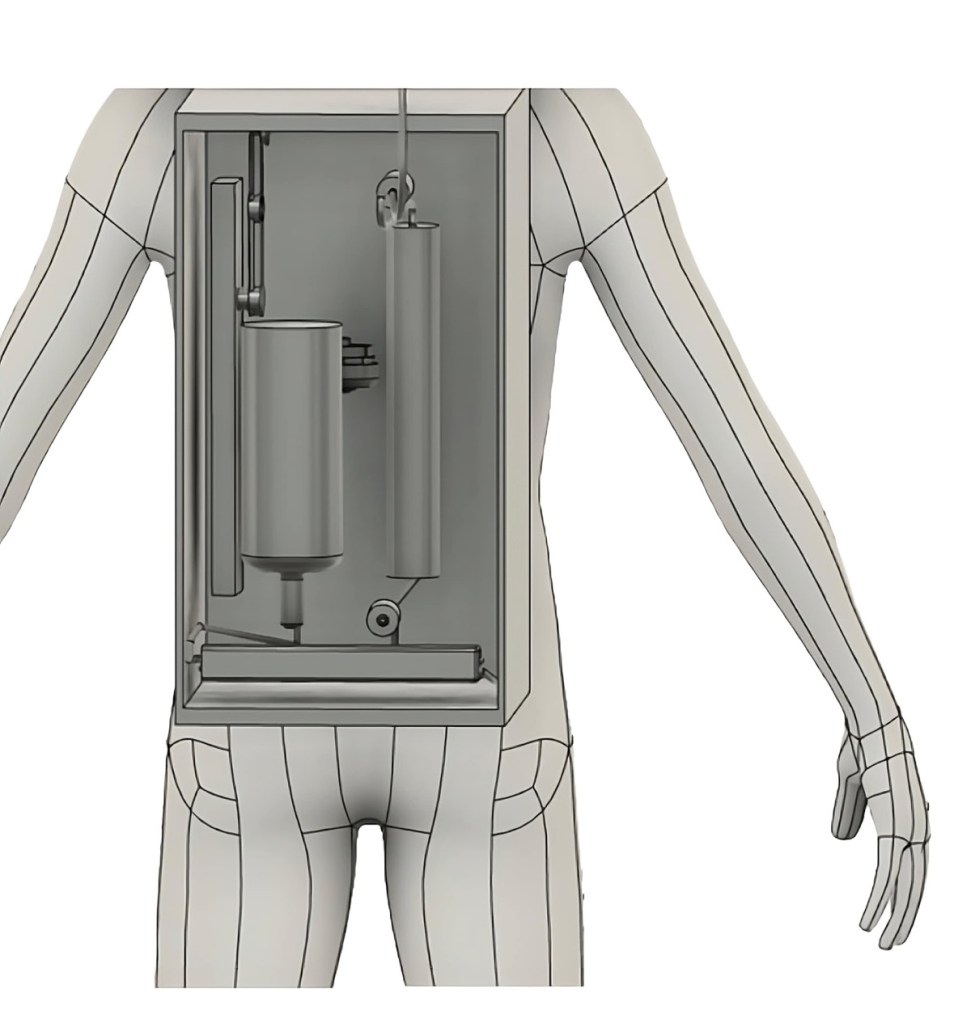
According to the proposed plan, the first part of the UFS will involve a FO unit. A section of this unit will consist of a highly saline and concentrated solution, also called a ‘draw solution’ in technical terms. The urine water or ‘feed solution’ flowing into the remaining section of this unit will undergo forward osmosis. The resulting draw solution will then be transferred to a section of the RO unit where it will act as a feed solution. This feed solution will be pressurized so that only pure water passes through the semi-permeable membrane into the remaining section of the RO unit leaving all the dissolved salts and impurities like Urea behind. This desalinated water would be potable and then enriched with electrolytes before being available for astronauts to drink. According to the research paper, this UFS will purify water with up to 87% efficiency and can be easily worn as a backpack or attached to the spacesuit itself.
Final thoughts

As of now, this portable water purification system is still on paper and it took a few years for something like this to materialise. A prototype is in the works, which will have to undergo multiple tests, including one in zero gravity. As NASA plans to resume its manned missions to the moon with the Artemis program along with plans for manned Martian missions in the next decade, a water filtration system of this kind, built inside a space suit will be extremely beneficial for the astronauts. A significant amount of water could be conserved and astronauts could spend much longer time outside the confines of their base without worrying about nature’s call or thirst.
References
- https://phys.org/news/2024-07-real-life-stillsuit-dune-spacesuits.html
- https://arstechnica.com/science/2024/07/scientists-built-real-life-stillsuit-to-recycle-astronaut-urine-on-space-walks/
- https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/space-technologies/articles/10.3389/frspt.2024.1391200/full
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35878521/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41545-021-00143-0
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304710851_Efficiently_Combining_Water_Reuse_and_Desalination_through_Forward_Osmosis-Reverse_Osmosis_FO-RO_Hybrids_A_Critical_Review
![Create a logo for a science-focused website [that embodies innovation] [and curiosity] [while exuding a modern and sleek aesthetic] that reflects a passion for scientific exploration. [It should integrate scientific elements] [and incorporate a sense of discovery].](https://scie99.blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/img-hxn9yfw6zqxcvavcolisqsxq.png)
Leave a reply to Vishal Kumar Cancel reply